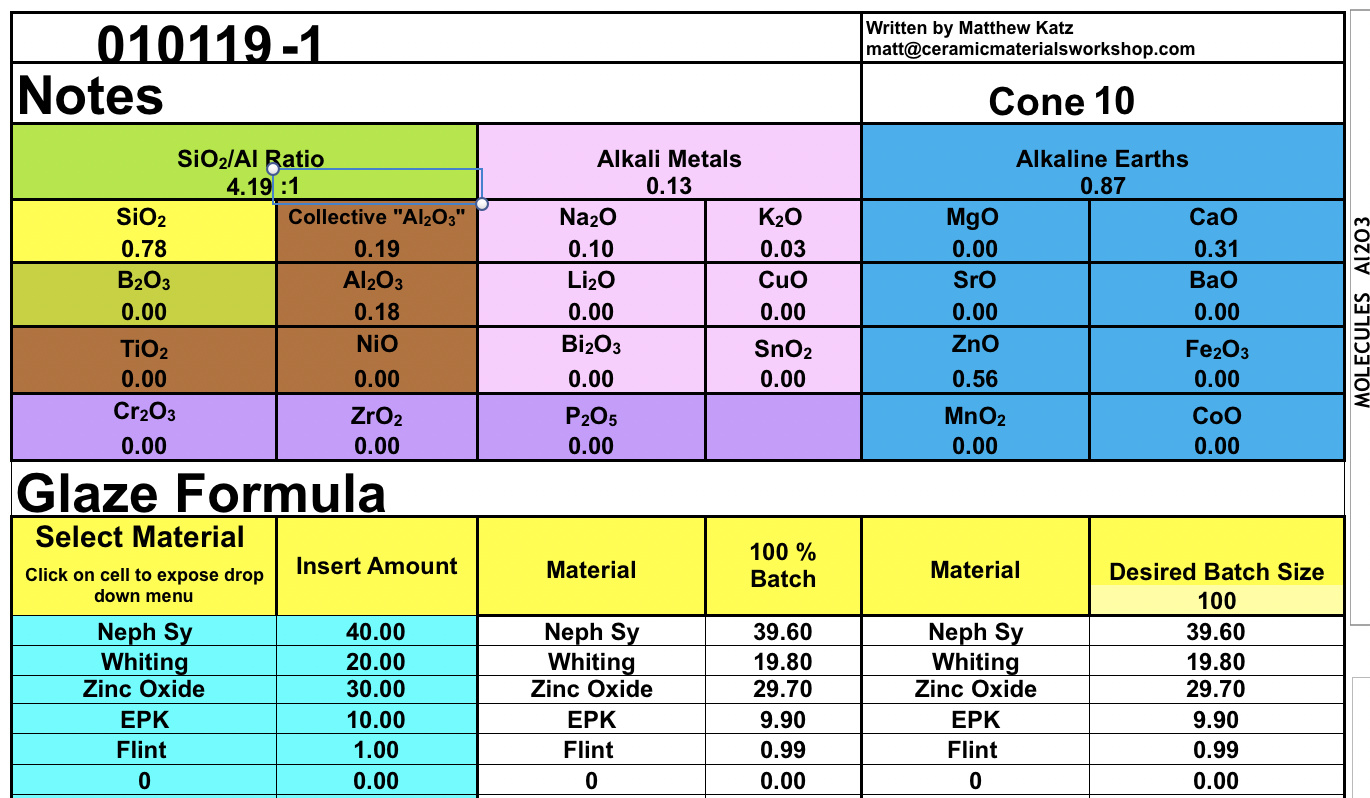
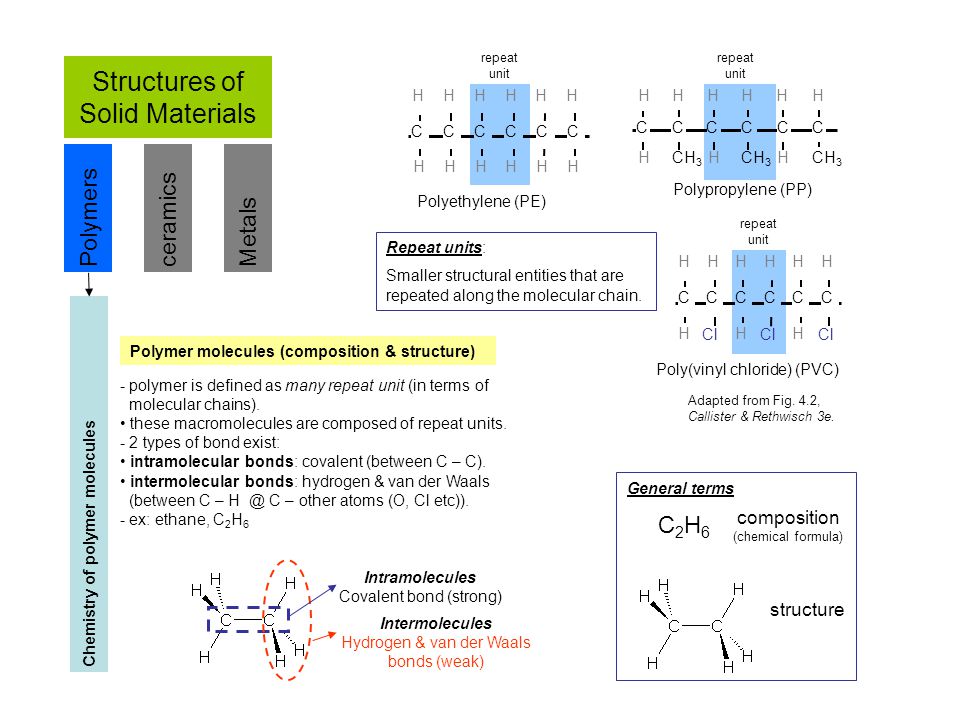
The average molecular weight can range from a few thousand to approximately 100 000 g mol while the density normally lies around 1 g cm 3.
Definition of molecular weight in ceramics.
The state of aggregation and the viscosity are both dependent on the molecular mass and the molecular macrostructure.
A ceramic material is an inorganic non metallic often crystalline oxide nitride or carbide material.
Kaolinite ˈ k eɪ ə l ɪ n aɪ t is a clay mineral part of the group of industrial minerals with the chemical composition al 2 si 2 o 5 4 it is a layered silicate mineral with one tetrahedral sheet of silica sio 4 linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina alo 6 octahedra.
Preparation of composite membranes.
The weight of larger molecules and macromolecules e g dna proteins is found using light scattering and viscosity.
They withstand chemical erosion that occurs in other materials subjected to acidic or caustic environments.
For oxidation reduction reactions one equivalent donates or.
Molecular weight definition is the average mass of a molecule of a compound compared to 1 12 the mass of carbon 12 and calculated as the sum of the atomic weights of the constituent atoms.
Zirconium dioxide zro 2 sometimes known as zirconia not to be confused with zircon is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium its most naturally occurring form with a monoclinic crystalline structure is the mineral baddeleyite a dopant stabilized cubic structured zirconia cubic zirconia is synthesized in various colours for use as a gemstone and a diamond simulant.
Mass spectrometry is commonly used to find the molecular mass of small to medium sized molecules.
Rocks that are rich in kaolinite are known as kaolin ˈ k eɪ ə l ɪ n or china clay.
Some elements such as carbon or silicon may be considered ceramics ceramic materials are brittle hard strong in compression and weak in shearing and tension.
The most important pre ceramic polymers are polysilanes.
For acid base reactions one equivalent donates or receives a mole of protons and the equivalent weight is the ratio of the molecular weight to the number of protons involved in the reaction.
How molecular weight is determined.
Number average molecular weight viscosity molecular weight weight average molecular weight z average molecular weight there are multiple definitions because different techniques for measuring molecular weight yield different results.
Definitions of molecular weight sperling 78 rodriguez 117 there are several ways to define molecular weight.
Empirical data on the molecular weight of a compound depends on the size of the molecule in question.