Initial chapters review biomedical applications and types of ceramics with subsequent sections focusing on the properties of ceramics and on corrosion degradation and wear of ceramic biomaterials.
Degradation of ceramic biomaterials.
Ceramic ceramic composites enjoy superiority due to similarity to bone minerals exhibiting biocompatibility and a readiness to be shaped.
Among these composites ceramic polymer composites have been found to release toxic elements into the surrounding tissues.
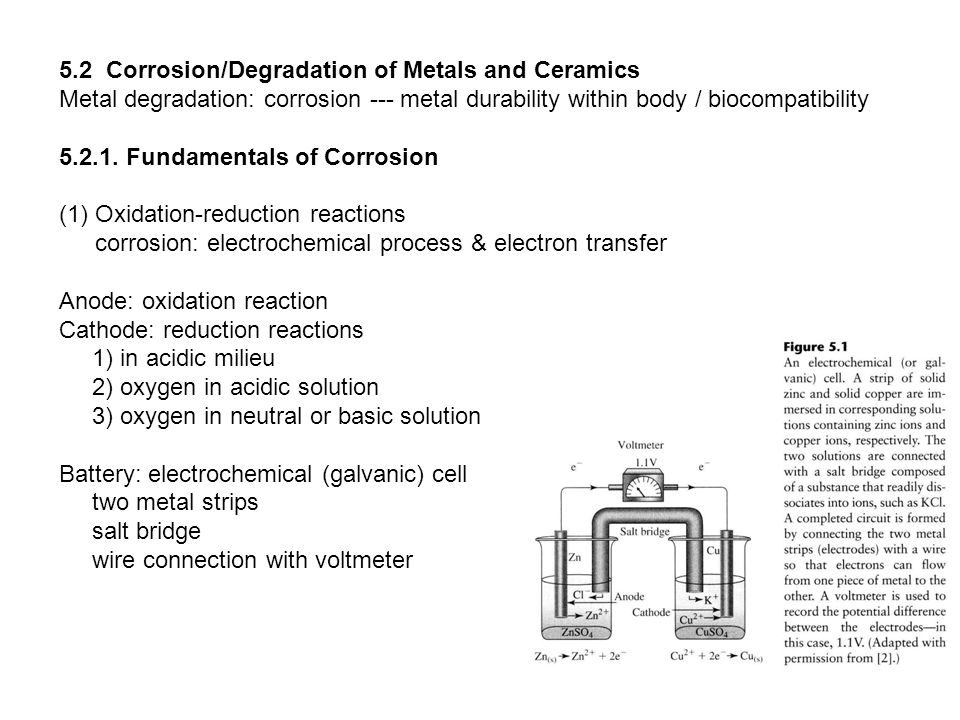
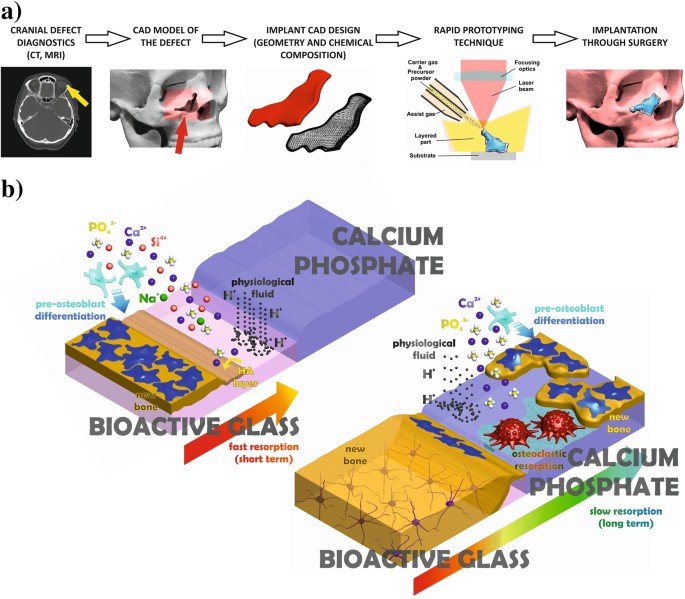
Metals face corrosion related problems and ceramic coatings on metallic implants degrade over time during lengthy applications.
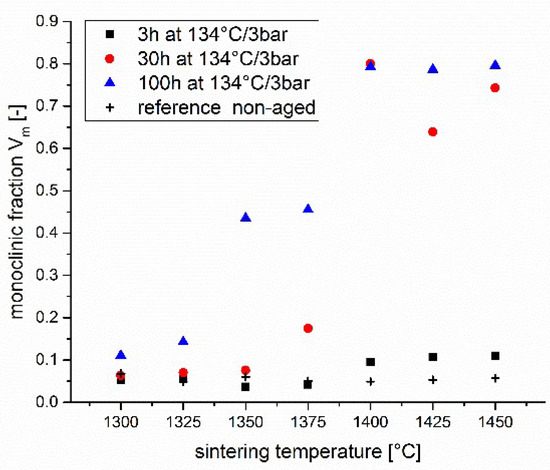
Even though the term corrosion was generally associated with metals ceramic materials are also undergone unintentional degradation in contact with environment.
The crystalline and amorphous states are typical solid states which represent the degree of order between ions atoms or molecules.
Ceramic biomaterials also stimulate bone growth and have low friction coefficients.
Initial chapters review biomedical applications and types of ceramics with subsequent sections focusing on the properties of ceramics and on corrosion degradation and wear of ceramic biomaterials.
Degradation mechanisms of bioceramics ceramic materials are held together by either ionic or covalent bonds.
Ceramics provides current information on ceramics and their conversion from base materials to medical devices.
They can be crystalline or amorphous.
They do not create strong biologically relevant interfaces with bones but they do promote strong adhesions to bones 3 the main applications of ceramic biomaterials include.
Ceramic biomaterials bioceramics the class of ceramics used for repair and replacement of diseased and damaged parts of the musculoskeletal system are referr slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance and to provide you with relevant advertising.